The Cooling Degree Days (CDD) method is a key technique for assessing a building’s cooling needs. This article explores the CDD method and demonstrates how Enectiva can automate CDD calculations using local weather station data and configurable parameters.
What is the Cooling Degree Days Method?
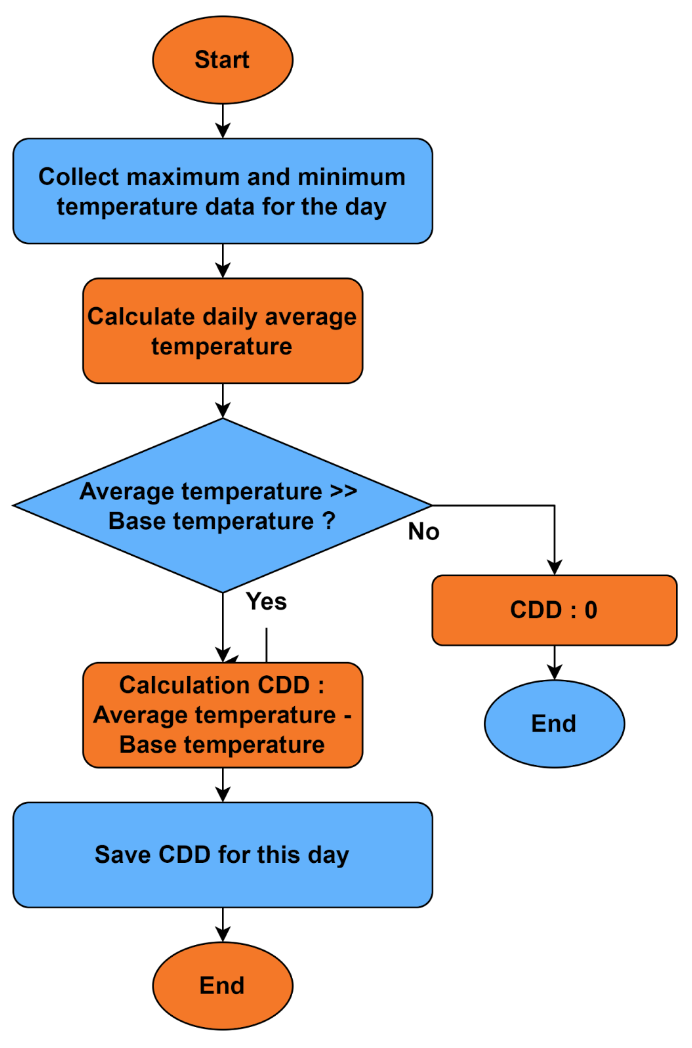
The cooling degree day method is used to estimate the cooling requirements of a building. It is based on the difference between the daily average outdoor temperature and a reference temperature, often called the “base temperature”. The higher the outdoor temperature is compared to the base temperature, the greater the number of cooling degree days.

How to Calculate Cooling Degree Days?
The calculation of CDD follows these steps:
- Define the base temperature (e.g., 24°C).
- For each day, subtract the base temperature from the average outside temperature.
- If the result is positive, it represents the cooling degree days for that day. If the result is negative then the CDD for that day is 0.
Example Table: CDD Calculation
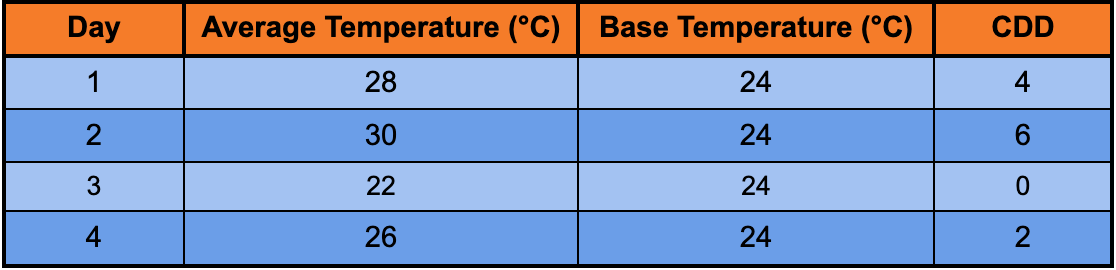
In this example, the number of CDD for these 4 days is 12.
Benefits of Using Enectiva for CDD
Enectiva makes CDD calculations easy by:
- Weather Data Integration: Enectiva integrates data from local weather stations for accurate calculations.
- Customizable Parameters: Adjust the base temperature according to the building’s needs.
- Detailed Reports and Analysis: Enectiva provides insights to optimize cooling and reduce energy costs.
By using Enectiva, building managers can automate CDD calculations and enhance cooling efficiency.
For more information or to get started, contact us directly at sales@enectiva.com or +420 222 766 950.
Let’s create a more efficient and sustainable future together.